Dr. Barry Citron and Dr. Cheryl Citron are proud to offer plastic surgery and dermatology solutions to patients in West Orange, Short Hills, and nearby areas in New Jersey. Click on the conditions below to learn more about what they are and what kind of treatments are offered here at Citron & Citron.
Have Questions? Click Here To Schedule a Consultation »
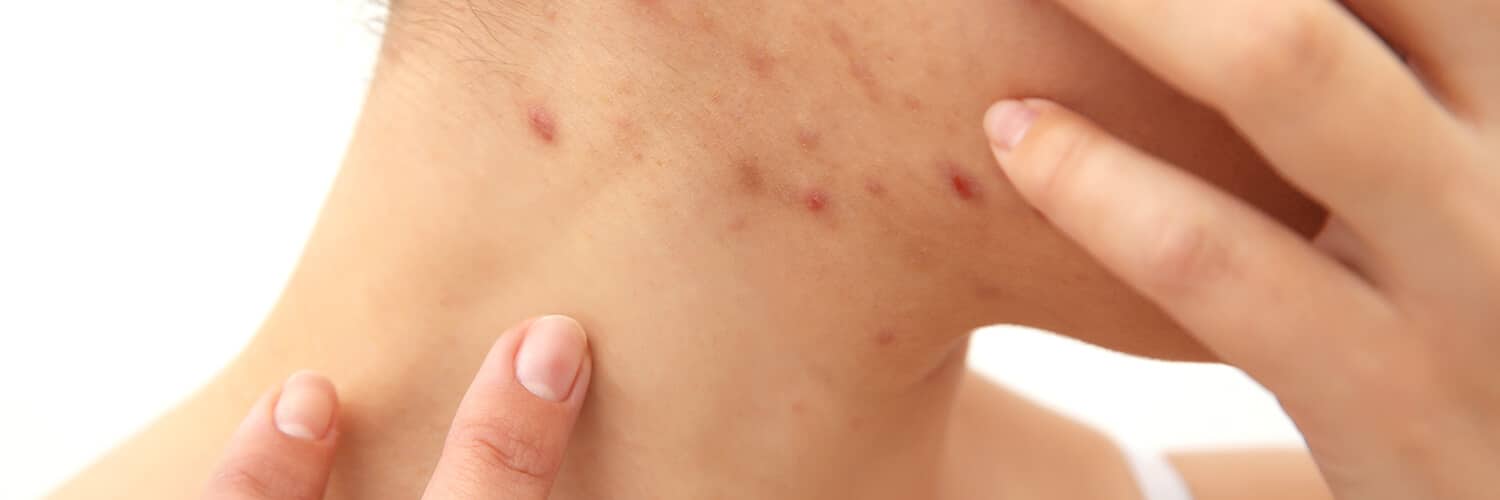
Acne
Acne is the term for the blocked pores (blackheads and whiteheads), pimples, and deeper lumps (cysts or nodules) that can appear typically on the face, neck, chest, back, shoulders and upper arms. Seventeen million Americans currently have acne, making it the most common skin disease in the country. While it affects mostly teenagers, and almost all teenagers have some form of acne, adults of any age can have it. Acne is not life-threatening, but it can cause physical disfigurement (scarring) and emotional distress.
Treatment for Acne
Treatment for acne varies depending on the type and severity of lesions, as well as the patient’s skin type, age and life. Options include:
- Topical Medications
- Antibiotics
- Accutane
- Blackhead Extraction
- Microdermabrasion
- Photodynamic Therapy
- Skin Care
- Blu-U Light Treatments
- Laser Treatments
Acne scarring can be treated in a variety of ways as well. These include:
- Chemical Peels
- Dermabrasion/Microdermabrasion
- Soft Tissue Fillers
- Laser/Pulsed Light Treatments
Eczema
What is Eczma?
Eczema is a group of inflamed skin conditions that result in chronic itchy rashes. About 15 million people in the U.S. suffer from some form of eczema, including 10-20 percent of all infants. Symptoms vary from person to person but often include dry, red, itchy patches on the skin which break out in rashes when scratched.
Objects and conditions that trigger itchy eczema outbreaks may include rough or coarse materials touching the skin, excessive heat or sweating, soaps, detergents, disinfectants, fruit and meat juices, dust mites, animal saliva and danders, upper respiratory infections and stress.
Treatment for Eczema
Treatment involves the restriction of scratching, use of moisturizing lotions or creams, cold compresses and nonprescription anti-inflammatory corticosteroid creams and ointments. If this proves insufficient, physicians may prescribe corticosteroid medication, antibiotics to combat infection, or sedative antihistamines. Phototherapy is a common procedure that uses light to reduce rashes. For severe cases, drugs such as cyclosporine A may be recommended.
Psoriasis
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a group of chronic skin disorders that cause itching and/or burning, scaling and crusting of the skin. Over seven million men and women in the U.S. of all ages have some form of psoriasis, which may be mild, moderate or severe. The most commonly affected areas are the scalp, elbows, knees, hands, feet and genitals.
Treatment for Psoriasis
Psoriasis cannot be cured but it can be treated successfully, sometimes for months or years at a time and occasionally even permanently. Treatment depends on the type, severity and location of psoriasis. The patient’s age, medical history and life may also have a significant impact on the methods utilized. The most common treatments are topical medications, phototherapy, photochemotherapy (PUVA), and oral or injectable medication (for severe symptoms).
Rash
What is A Rash?
A rash is a change in the skin’s color or texture. Simple rashes are called dermatitis, which means the skin is inflamed or swollen. Contact dermatitis is caused by touching an irritating substance such as clothing materials and dyes, latex, cosmetics, soaps or certain plants like poison ivy. Seborrheic dermatitis forms red patches and scaling, usually on the face and head, where it is more commonly known as dandruff or cradle cap. Other common rashes include eczema, psoriasis, impetigo, shingles, chicken pox, measles, scarlet fever, insect bites and those caused by medical conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment for Rashes
A dermatologist is usually able to identify the rash by looking at it and asking about accompanying symptoms. Mild rashes can often be treated with simple home care practices such as avoiding soaps and bathing in warm water. Others may require moisturizing creams, prescription medications or more extensive treatment.
Rosacea
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes redness and swelling on the face and occasionally on the neck, ears, chest, back and eyes as well. The specific cause of rosacea is unknown, but is suspected to involve a combination of hereditary and environmental factors, and is most common in fair-skinned adults between the ages of 30 and 50. Certain triggers, such as consuming alcohol or spicy foods, may worsen symptoms of rosacea.
Treatment for Rosacea
Treatment for rosacea aims to relieve symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. This can be done through a combination of approaches, including topical and oral medications, antibiotics, Accutane, or surgery for severe or permanent symptoms. Your doctor will develop a customized treatment plan after a thorough evaluation of each patient’s individual condition. While there is no cure for rosacea, many patients can achieve effective symptom relief for long periods of time.
Warts
What Are Warts?
Warts are a common condition that develops on different areas of the body as a result of infection by a type of human papillomavirus (HPV). There are several different types of warts, which may have a different appearance and tend to occur in different areas. In general, warts tend to appear on warm, moist parts of the body, such as the hands, feet knees and elbows.
Although they can affect anyone, warts are most common in children and young adults, as they are passed through direct contact with an infected area. Warts often appear as small skin growths that may be flat or slightly raised, and can be brown, gray, pink or skin-colored. Your doctor can diagnose warts through a simple physical exam.
Treatment for Warts
While warts are not usually considered harmful, they may be painful or embarrassing and should be thoroughly treated to relieve symptoms and prevent them from spreading to other people or other parts of the body. Most warts can be treated through conservative methods such as applying salicylic acid or cantharidin or by undergoing cryotherapy (freezing) treatments. Resistant warts may require surgical treatment through excision or laser surgery.
Your doctor will determine the most effective treatment option for you after a thorough evaluation of your condition. In most cases, treatment is permanent and warts do not return. There are certain preventive measures that can be taken to prevent warts from spreading, including avoiding sharing towels, razors and other personal items.
Schedule Your Facelift Consultation Today!
Interested in learning more about the conditons we treat? Give us a call at 973-243-2300 or schedule your consultation here. We serve West Orange, Short Hills, and nearby areas in New Jersey!
